Service¶
This page describes the service architecture and its specifications.
The service is a FastAPI application that is deployed on a Kubernetes cluster. It is a REST API that can be used to process data.
Architecture¶
To see the general architecture of the project, see the global UML Diagram.
This sequence diagram illustrates the interaction between an user and a service, without using the Core engine.
sequenceDiagram
participant S as s - Service
participant C as c - Client
participant S3 as s3 - Storage
C->>+S3: file_keys = for file in data: upload(file)
S3-->>-C: return(200, file_key)
C->>+S: POST(s.url/process, callback_url: str, service_task: ServiceTask)
Note right of S: callback_url is the url where the service should send the response
Note right of S: service_task should match the model
S-->>-C: return(200, Task added to the queue)
S->>+S3: data = for key in service_task.task.data_in: get_file(service_task.s3_infos, key)
S3-->>-S: return(200, stream)
S->>S: result = process(data)
S->>+S3: data_out = for res in result: upload_file(service_task.s3_infos, data_out)
S3-->>-S: return(200, key)
S->>S: task_update = jsonable_encoder(TaskUpdate({status: finished, task.data_out: data_out}))
S->>+C: PATCH(callback_url, task_update)
C-->>-S: return(200, OK)
C->>+S3: GET(task_update.data_out)
S3-->>-C: return(200, stream)Specifications¶
Inside the project, the services are implemented using Python. But the service is a REST API, so it can be implemented in any language.
Endpoints¶
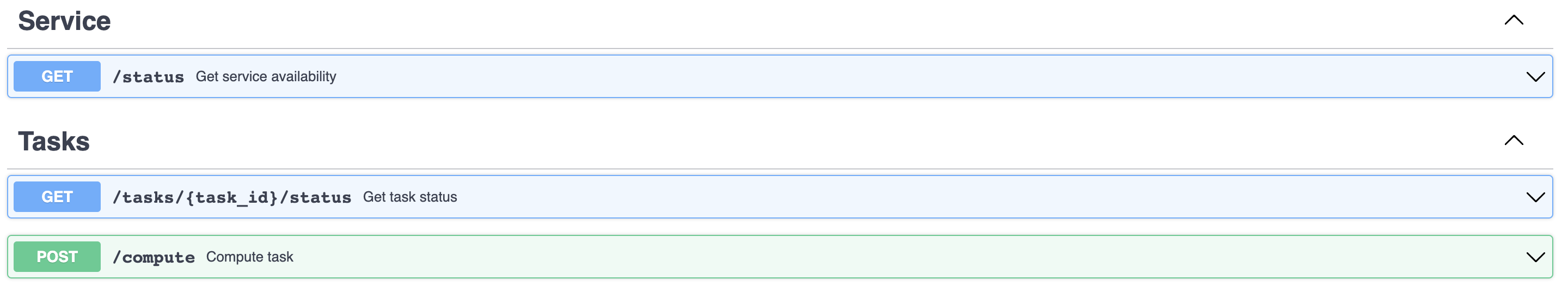
To match the specifications, the service must implement the following endpoints:
- GET
/status: returns the service availability. (Returns a string) - GET
/tasks/{task_id}/status: returns the status of a task. (Returns a string) - POST
/compute: computes the given task and returns the result. (Returns a string)
Models¶
The different models used in the pipeline are described below.
Task Input¶
The POST /compute endpoint must be able to receive a JSON body that matches the following model:
The data_in and data_out fields are lists of S3 object keys. The status field is a string that can be one of the following values:
The S3 settings are used to connect to the S3 storage where the data is stored and where the result will be stored. The callback_url is the url where the service should send the response.
A JSON representation would look like this:
Task Output¶
Once the task is computed, the service must PATCH the task on /tasks/{task_id} with the following model:
The data_out field is a list of S3 object keys. The status field is a string that can be one of the following values:
A JSON representation would look like this:
Register to the Core engine¶
To register the service to the Core engine, the service must send a POST request to the Core engine /services endpoint with the following model:
The data_in_fields and data_out_fields fields are lists of FieldDescription models. A FieldDescription model is defined as follows:
The url field is the url of the service.
A JSON representation would look like this:
After the service is registered, it will be available on the Core engine's /service-slug endpoint.
Environment variables¶
All environment variables are described in the .env file at the root of the repository.
The values can be changed for local development. For example, to have multiple services running on the same machine, The SERVICE_PORT variable can be changed to a different port number.
Run the tests with Python¶
Info
You might need to initialize a virtual environment before running the tests.
Check the Start the service locally > Start the service locally with plain Python to initialize and activate a virtual environment.
For each module a test file is available to check the correct behavior of the code. The tests are run using the pytest library with code coverage check. To run the tests, use the following command inside the service folder:
Start the service locally¶
Tip
If you are not familiar with the Core engine and its services, we recommend to follow the Getting started guide first.
The Core engine is highly recommended to test the service locally.
You have several options to start the service locally:
- Start the service locally with Docker Compose (recommended)
- Start the service locally with plain Python
- Start the service locally with minikube and official Docker images
- Start the service locally with minikube and local Docker images
In the service directory, start the service with the following commands:
Access the service documentation at http://localhost:9090/docs.
Access the Core engine on http://localhost:3000 or http://localhost:8080/docs to validate the service has been successfully registered to the Core engine.
In the service directory, start the service with the following commands:
Start the application.
Access the service documentation on http://localhost:9090/docs.
Access the Core engine on http://localhost:3000 or http://localhost:8080/docs to validate the service has been successfully registered to the Core engine.
Start the service with the following commands. This will start the service with the official Docker images that are hosted on GitHub.
In the service directory, start the service with the following commands:
Create a tunnel to access the Kubernetes cluster from the local machine. The terminal in which the tunnel is created must stay open:
Access the service documentation on http://localhost:9090/docs.
Access the Core engine on http://localhost:3000 or http://localhost:8080/docs to validate the service has been successfully registered to the Core engine.
Warning
The service StatefulSet (stateful.yml file) must be deleted and recreated every time a new Docker image is created.
Start the service with the following commands. This will start the service with the a local Docker image for the service.
In the service directory, build the Docker image with the following commands.
In the service directory, start the service with the following commands.
Create a tunnel to access the Kubernetes cluster from the local machine. The terminal in which the tunnel is created must stay open.
Access the service documentation on http://localhost:9090/docs.
Access the Core engine on http://localhost:3000 or http://localhost:8080/docs to validate the service has been successfully registered to the Core engine.